Break-Even Analysis: Formula and Calculation

A business would not use break-even analysis to measure its repayment of debt or how long that repayment will take. Break-even analysis is a tool that can be used to demonstrate and calculate how much revenue is needed to make a certain amount of profit, assuming expenses remain constant. If you’re looking for other small business tips and accounting tools, we’re here to help. QuickBooks can assist with tasks from bookkeeping and payroll to inventory analysis and profitability.
Focus on a single product or service
Thus, the unit variable costs to make a single dress is $110 ($60 in materials and $50 in labor). For options trading, the breakeven point is the market price that an underlying asset must reach for an option buyer to avoid a loss if they exercise the option. The breakeven point doesn’t typically factor in commission costs, although these fees could be included if desired. Note that in the prior example, the fixed costs are “paid for” by the contribution margin.
What Is Break-Even Analysis?
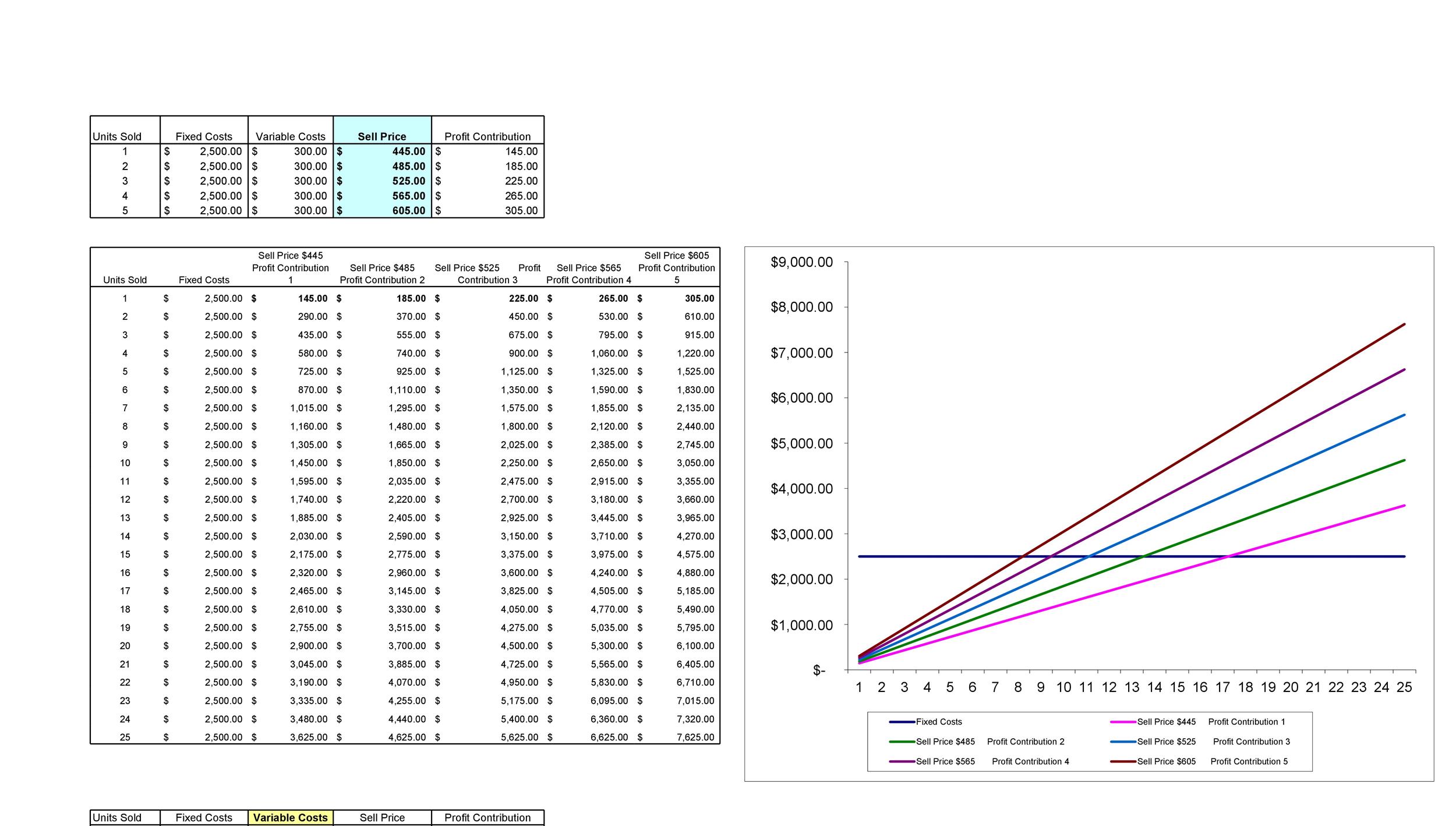
Break-even analysis assumes that per unit selling price and variable cost do not change, which is not always the case. These costs stay the same regardless of how many units the company is producing. These include start-up costs, and other capital expenses which do not have to be paid periodically. Rent, insurance, utility bills and repairs are also considered fixed costs, since variations are minute and the amount does not directly depend on the number of items produced. For example, if a tire manufacturer rents a building at $2000 per month, and decides to produce 100 tires, the fixed cost will be $2000. The amount will stay the same if even there is no activity and zero tires are produced.
Contribution Margin
- The above example shows how an improvement in actual sales improved margin of safety for the business as the sales improved.
- In this breakeven point example, the company must generate $2.7 million in revenue to cover its fixed and variable costs.
- The key thing to remember is that it’s a ratio of your fixed and variable costs.
- Tracking this data over time can help you identify patterns — e.g., slower sales during specific months — so you can adjust your strategy based on those trends.
- This tool fails to take into account the demand-side situation, since not all units produced are sold at the assumed price.
Another limitation is that the breakeven point assumes that sales prices, variable costs per unit, and total fixed costs remain constant, which is often not the case. The price of goods sold at fluctuates, and the cost of raw materials may hardly stay stable. In addition, changes to the relevant range may change, meaning fixed costs can even change. This makes it almost impossible to always have a most up-to-date, accurate breakeven point. This margin indicates how much of each unit’s sales revenue contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit once fixed costs are met.
Graphical Representation of Break-even Analysis
A break-even analysis helps business owners find the point at which their total costs and total revenue are equal, also known as the break-even point in accounting. This lets them know how much product they need to 9 ways to finance a business sell to cover the cost of doing business. It is essential that the results from break-even analysis are interpreted correctly and the information is effectively utilized to make better, informed business decisions.
Benefits of break-even analysis
Typically, this analysis works best for businesses that focus on a single product or service. The analysis becomes more complex and less accurate if you offer a wide range of products with different price points and variable costs. For example, If you sell both high-end electronics and low-cost accessories, a single break-even analysis won’t account for the differing profit margins. You’d need individual analyses for each product category to get a more accurate picture of your profitability.
In accounting terms, it refers to the production level at which total production revenue equals total production costs. In investing, the breakeven point is the point at which the original cost equals the market price. Meanwhile, the breakeven point in options trading occurs when the market price of an underlying asset reaches the level at which a buyer will not incur a loss. If the company can increase its contribution margin per unit to $8 (by perhaps lowering its per unit variable cost), it only needs to sell 8,750 ($70,000 / $8) to break even.
Break-even analysis, also known as break-even point analysis, involves calculating the point at which a business breaks even and what steps it might take to become profitable. Also, remember that this analysis doesn’t take into consideration the present vs. future value of your funds. See the time value of money calculator for more information about this topic. The standard break-even period is hard to predict and fully depends on your business. However, once you know your break-even point, you can gauge the time it will take to break even more accurately. Risk comes in various forms, but break-even points can help you understand the viability of certain products before they’re even launched.
