Breakeven Point: Definition, Examples, and How to Calculate

Don’t worry, we will explain with examples below.Revenue is the income, or dollars made by selling one unit. A simpler version of the break-even chart is known as the profit-volume graph (P/V graph). This graph shows a direct relationship between sales and profits, and it is easy to understand.
Using break-even analysis to determine level of production
Another important aspect of business transaction that is missed in break-even calculation is principal balance of outstanding loans. The interest being paid on all loans should be part of fixed costs, but it is shown as an expense in the profit & loss account. As it can be seen from the above example that, higher the selling price of a particular product, the break-even point is lower. Assume that an investor pays a $5 premium for an Apple stock (AAPL) call option with a $170 strike price.
Why Embracing Financial Forecasts Will Make You a Better Advisor
The break-even point is the condition of a company or business before it starts to gain profit. This dataset includes the Sales Quantity in units, the Unit Selling Price, the components of Fixed Cost, and the components of Variable Cost. If a business is at the precise break-even point, the business is neither running at a profit nor at a loss; it has simply broken even.
Entering Formulas
Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. This section provides an overview of the methods that can be applied to calculate the break-even point.
- However, the graph can be interpreted only within the relevant range of operations (i.e., the level of activity over which fixed costs are assumed to remain fixed).
- Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
- Hence, this tool provides more information for the mangers to make better pricing decision, considering the supply-side of the production process.
- The break-even point is the point at which there is no profit or loss.
If you’re seeking funding for your business, this information is often expected or required by lenders and investors. It helps them gauge the viability of your idea and determine what level of funding is appropriate. For you as a business owner, it can help you determine how much funding you think you’ll need and even identify how you’ll use those funds.
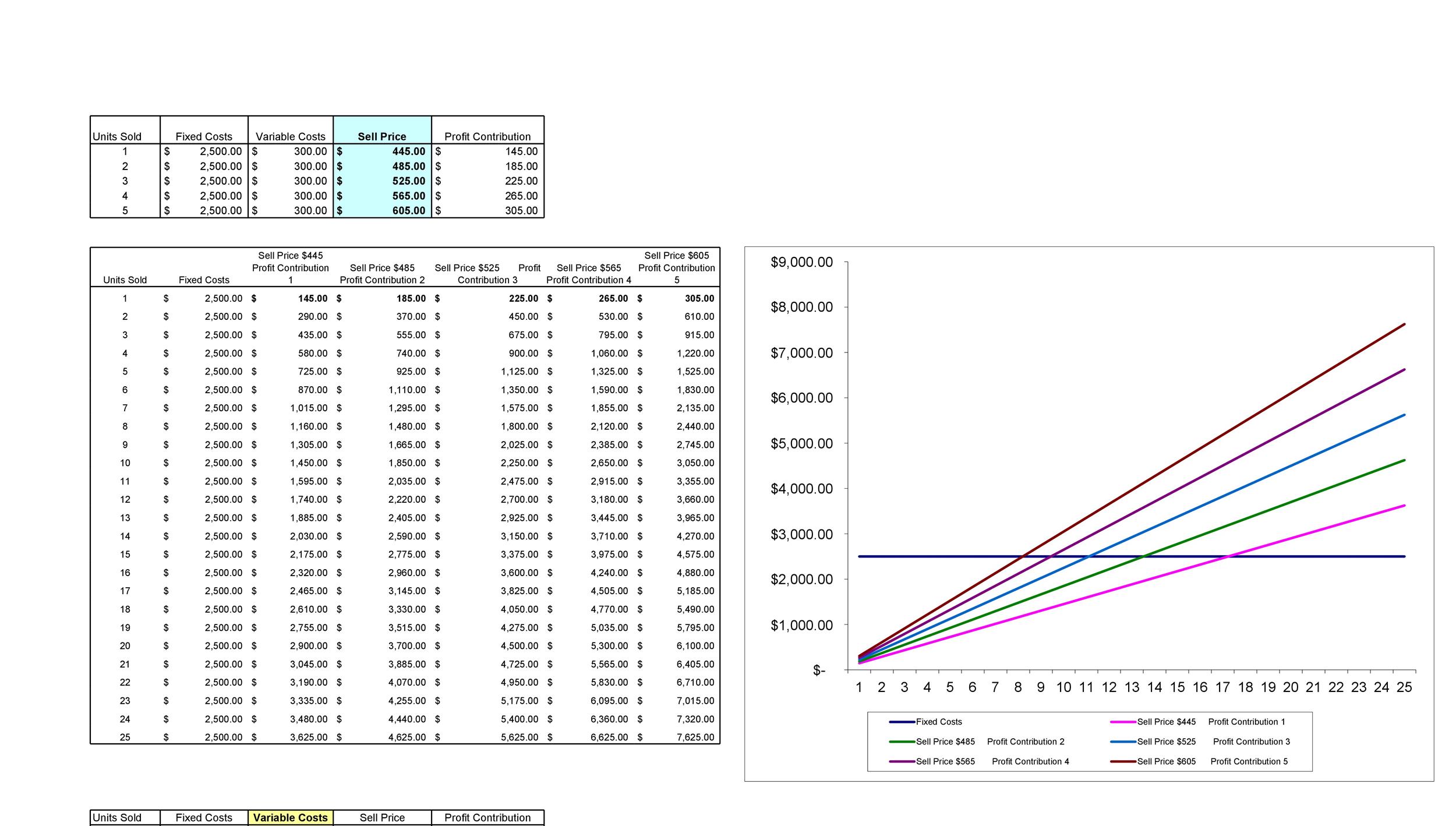
Today, 30% of our visitors use Ad-Block to block ads.We understand your pain with ads, but without ads, we won’t be able to provide you with free content soon. If you need our content for work or study, please support our efforts and disable AdBlock for our site. The data used to prepare the break-even chart, as shown above, have also been used to prepare the P/V graph shown below.
For example, you may find that your product is unprofitable at a certain price point except at extremely large scales. Conducting a break-even analysis is a crucial tool for small business owners. This gives you the number of units you need to sell to cover your costs per month. The break-even point is this philip campbell author at financial rhythm page example is 100,000 units because it is the output level at which the total revenue and total cost curves intersect. Break-even point calculation is a rather simple calculation that can help businesses with forecasting costs and sales. As mentioned earlier, break-even point there is no profit, no loss.
By plugging different Q values, we can create a table of total revenue and total costs, which may be bifurcated into total variable costs and total fixed costs. Break-even analysis, or the comparison of sales to fixed costs, is a tool used by businesses and stock and option traders. It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even. It is also possible to calculate how many units need to be sold to cover the fixed costs, which will result in the company breaking even. To do this, calculate the contribution margin, which is the sale price of the product less variable costs.

